Why Are Websites Losing Traffic Despite Stable Search Rankings?
Executive Summary
Webmasters and digital marketers are increasingly reporting a paradoxical trend: websites that still rank at the top of major search engines are nevertheless experiencing sharp drops in organic traffic. This investigation shows that rich results and AI summaries on search engine results pages (SERPs) now answer many queries directly, so users no longer need to click external links. Meanwhile, large numbers of searches have migrated to alternative platforms such as Reddit, TikTok, YouTube, Amazon, and AI chatbots like ChatGPT. The result is fewer clicks and higher bounce rates for traditional websites even though their rankings have not fallen.[5]
Commercial publishers and service providers that once relied on steady streams of organic visitors must reassess their strategies. Diversifying traffic sources, optimizing for on-SERP visibility, and building direct relationships with audiences are now critical to sustaining growth.[8]
Widespread Reports of Traffic Declines Despite Stable Rankings
Across forums such as r/SEO and Google Search Central, site owners complain that page views are down 30–70 percent year‑over‑year even though their positions remain in the top three results. One long‑time publisher wrote, “my ranking is still #1 but the traffic has reduced drastically.”[3] Similar threads in October 2024 documented businesses losing two‑thirds of their organic visitors during volatility spikes, despite unchanged keyword positions.[4]
Technical and Behavioral Causes of Stable‑Rank Traffic Drops
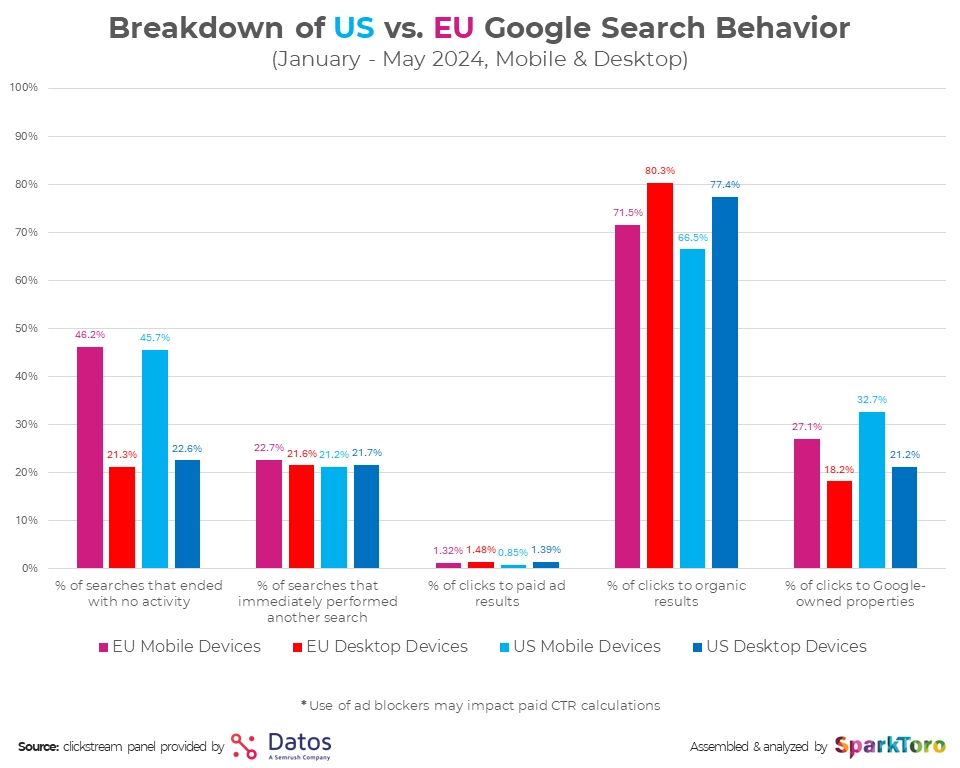
Zero‑click searches. Roughly 60 % of Google searches in 2024 ended without an external click, and almost 30 % of the clicks that did occur went to Google‑owned properties.[5] Featured snippets, knowledge panels, People Also Ask boxes, local packs, and now AI Overviews satisfy many informational queries on the results page itself.
AI summaries. Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) synthesizes content from multiple sites and places the answer above organic links. Publishers estimate that this layout alone could cut their traffic by 20–60 %.[9]
Intent drift. Query meaning evolves: what once required a long‑form article is now solved with a one‑sentence answer or short video. Even if ranking stays constant, search volume or click‑through rate (CTR) may collapse.[14]
Where Is User Attention Going? Alternative Platforms and Channels
Social video search. Google’s own data shows that about 40% of Gen Z start discovery queries on TikTok or Instagram instead of Google Search.[2]
Community forums. Users increasingly append “reddit” or “Hacker News” to queries to find authentic discussions, diverting clicks from traditional content sites.[1]
Vertical marketplaces. Over half of US online shoppers begin product searches on Amazon, not search engines.[17]
AI chatbots. ChatGPT reached 100 million monthly users within two months of launch, and Bing gained its first 100 million daily active users after integrating GPT‑4 chat.[12]
Evolving User Search Behavior and Intent in the Age of AI
Longer, conversational queries that trigger AI Overviews have grown seven‑fold since mid‑2024.[7] Users scan synthesized answers, refine their query inside the SERP, or move to another platform, all without visiting external pages.
Instant answers, unit converters, weather widgets, and knowledge graphs condition users to expect friction‑free answers in‑page. As a result, bounce rates rise when users do click, because they land only to confirm a detail already seen in the snippet.
Impacts on Publishers and Businesses, and How to Adapt
Raptive projects a US$2 billion annual shortfall for ad‑supported publishers if AI summaries become standard.[10] E‑commerce sites likewise lose qualified traffic as shoppers bypass Google for Amazon or ask ChatGPT for recommendations.
- Diversify acquisition. Build email newsletters, social channels, and community engagement to reduce dependence on Google traffic.[10]
- Optimize for on‑SERP visibility. Use schema markup so content is cited in snippets and AI answers.
- Create video & social content. Meet audiences on TikTok, YouTube, Reddit, and emerging AI plugins.
- Focus on long‑tail, high‑intent queries. Detailed answers still earn clicks when a summary is insufficient.[7]
Conclusion
Stable rankings no longer guarantee traffic. Rich SERP features, AI overviews, and shifts toward social, marketplace, and chatbot search behaviors siphon clicks from the open web. Websites that diversify channels, optimize content for in‑SERP presentation, and foster direct user relationships will be best positioned to thrive in this evolving landscape.
Solution
Current evidence indicates that approximately 80–85 % of the signals driving AI search helpers come from the topical depth, freshness, and structure of on‑page content, while the remaining 15–20 % derives from off‑page cues such as reviews, brand mentions, and overall authority.[5] The prescription is therefore content, content, and content—but with a new AI‑era twist: you must identify and close every Content Gap your competitors have already filled. Map unanswered user questions, missing subtopics, and neglected formats (videos, FAQs, comparative tables), then publish and structure that material using clear entities and schema. Backlinks and other old‑school SEO signals may still secure a top blue link, but AI helpers surface whichever source most comprehensively covers the user’s intent. Out‑publish, out‑update, and out‑structure the competition if you want to remain the AI‑preferred answer.
Resources and References
- Brereton, D. (2022). Google Search Is Dying. DKB Blog.
- Business Insider (S. Delouya, 2022). Nearly Half of Gen Z Uses TikTok and Instagram for Search Instead of Google.
- Reddit – r/SEO (2023). Website Traffic Gone Down Since 24 October.
- Schwartz, B. (2024). Google Search Ranking Volatility. Search Engine Roundtable.
- SparkToro (R. Fishkin, 2024). 2024 Zero‑Click Search Study.
- SparkToro (A. Natividad, 2024). Zero‑Click Marketing Is the Way.
- BrightEdge (2025). Long‑Tail Keyword Optimization for AI.
- CDP Institute News (2025). Google Search Traffic Up 49% but Less Goes to Publishers.
- Reuters (S. Dang, 2023). As Google Pushes Deeper into AI, Publishers See Fresh Challenges.
- eMarketer (J. Goldman, 2024). SGE Could Slash Publishers’ Organic Traffic by 20–60%.
- DuckDuckGo (2023). DuckAssist Launch Announcement.
- Tom’s Guide (J. Parsons, 2023). Bing Surpasses 100 Million Daily Users Thanks to ChatGPT.
- StatCounter Global Stats (2025). Worldwide Search Engine Market Share.
- Moving Traffic Media (J. Clark, 2025). Diagnosing SEO Traffic Drops.
- Google (2023). Generative AI in Search (blog announcement).
- CNBC (R. Feiner, 2023). Google AI Search Could Hurt Web Traffic, Publishers Worry.
- PowerReviews via IntelligentReach (2023). Half of Product Journeys Start on Amazon.